Physics - Grade XI or Standard XI
Chapter 3: Projectile Motion
Position:
The position of a point object at a given instant of time is a point in the space at which the object exists at that instant of time.
Displacement:
Displacement of a particle is the change in its position in a particular direction.
Path length:
Path length is the actual distance travelled by the particle during its motion.
Notice that path length and displacement are equal if object does not change its direction during the course of motion, otherwise path length is greater than displacement. Their SIU is m.
Average velocity:
Average velocity is defined as the change in the displacement divided by the time interval in which the displacement occurs. Its SIU is m/s.
Average speed:
Average speed of a particle is defined as the total path length travelled divided by total time interval during which the motion has taken place. Its SIU is m/s.
Instantaneous velocity:
Instantaneous velocity is defined as the velocity of object at a particular instant. Its SIU is m/s.
Instantaneous speed:
Instantaneous speed is the magnitude of instantaneous velocity. Notice that speedometer of a vehicle measures the instantaneous speed of the vehicle.
Acceleration:
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity w. r. t. (with respect to) time. Its SIU is m/s2.
Click Here to Go To Top of The Page
Instantaneous acceleration:
Instantaneous acceleration is defined as the acceleration of a particle at a particular instant. Its SIU is m/s2.
Uniform acceleration:
Acceleration is said to be uniform if the velocity changes by equal amount in equal intervals of time, however small or large the time interval may be. Its SIU is m/s2.
Kinematical equations
(bold letters represent vectors):
v = u + a . t (first kinematical equation)
s = u . t + (1/2) . a . t2 (second kinematical equation)
v2 = u2 + 2 . a . s (third kinematical equation)
where v = final velocity (at time = t), u = initial velocity (at time = 0), a = acceleration, t = time interval, s = displacement of projectile. In third equation a . s represents the dot product of two vectors.
Projectile:
An object thrown in the air with initial velocity in any direction, making some angle with the horizontal, moving freely under the action of gravity is called projectile.
Velocity of projection:
The velocity with which a body is projected is called as velocity of projection.
Angle of projection:
The angle made by the velocity of projection with the horizontal is called as the angle of projection.
Trajectory:
The path followed by the projectile in space is called as its trajectory.
Click Here to Go To Top of The Page
Equation of path of a projectile:
Equation of path of projectile is given below:
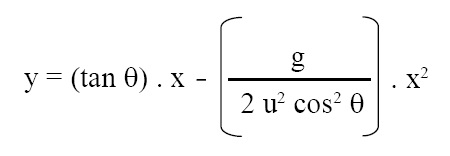
where y = vertical distance travelled by projectile, x = horizontal distance travelled by projectile, θ = angle of projection, g = gravitational acceleration due to earth, and u = velocity of projection.
Time of flight of projectile:
Time taken by the projectile to cover the entire trajectory is called as time of flight. It is given by the following expression:
T = 2 u sinθ / g
where T = time of flight of projectile, u = velocity of projection, θ = angle of projection, g = gravitational acceleration due to earth = 9.81 m/s2.
Horizontal range of projectile:
Horizontal distance between the point of projection and the point on the same horizontal plane, at which the projectile returns after moving along its trajectory, is called the horizontal range of the projectile. It is given by the following expression:
R = u2 sin2θ / g
where R = horizontal range of projectile, u = velocity of projection, θ = angle of projection, g = gravitational acceleration due to earth.
Click Here to Go To Top of The Page
Maximum height of projectile:
The maximum vertical distance travelled by the projectile from the ground level during its motion is called the maximum height of projectile. It is given by the following expression:
H = u2 sin2θ / (2g)
where H = maximum height of projectile, u = velocity of projection, θ = angle of projection, g = gravitational acceleration due to earth.
Angle of projection:
Expression for angle of projection is given below:
θ = tan-1(4H/R)
where θ = angle of projection, H = maximum height of projectile, and R = horizontal range of projectile.
Click Here to Go To Top of The Page